Automated Plant Watering System
Automates plant watering with a micro-controller, sensors, and actuators.
Image Gallery
Click on an image to read more about it.
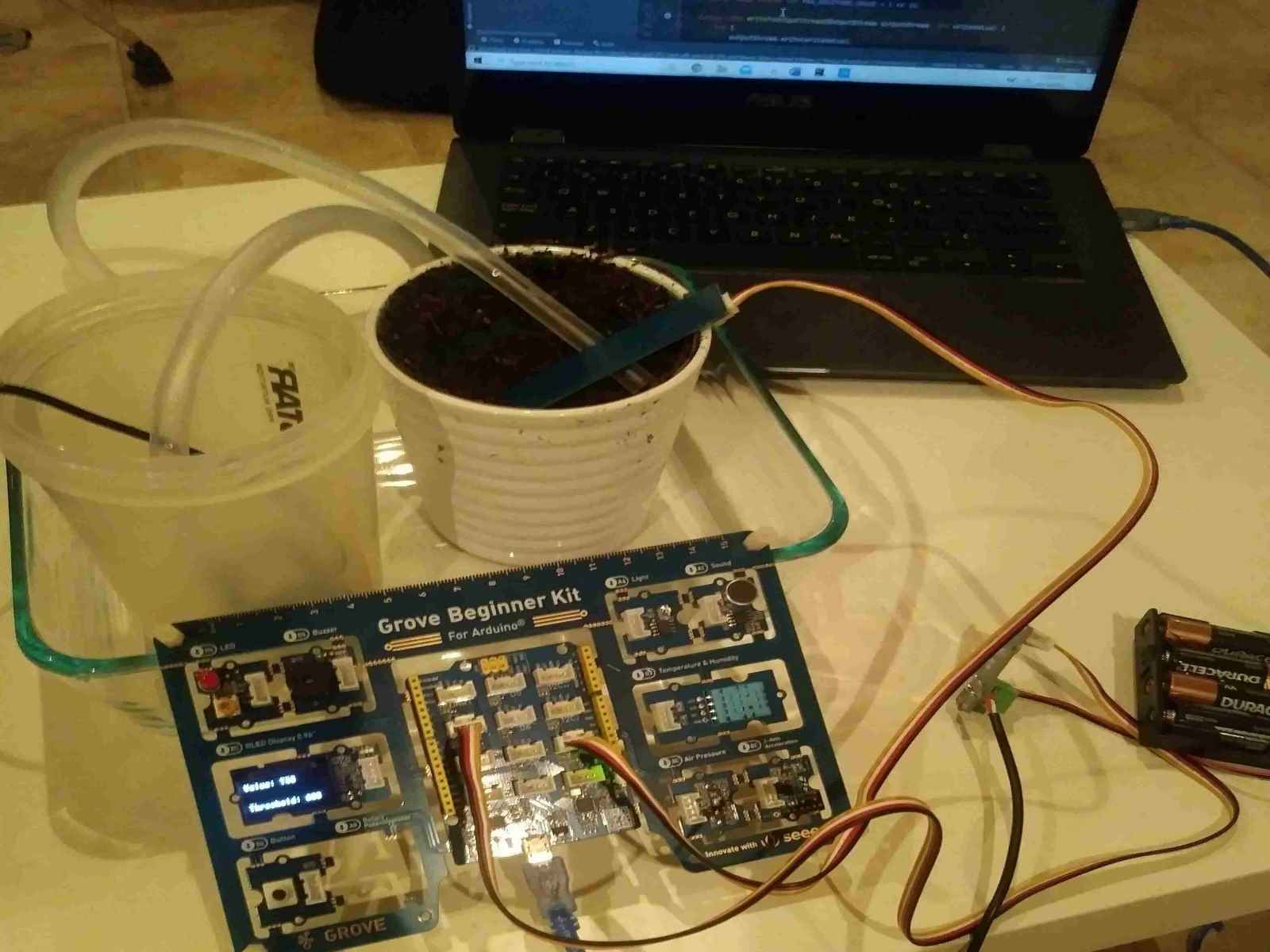

Automated Plant Watering System
This is the system when it still required the laptop to function. The Arduino is connected to a laptop running Java code which monitors the Arduino. The moisture sensor and pump connected to the Arduino are in the pot of soil, ready to water the plant.This is the system when it still required the laptop to function. The Arduino is connected to a laptop running Java code which monitors the Arduino. The moisture sensor and pump connected to the Arduino are in the pot of soil, ready to water the plant.
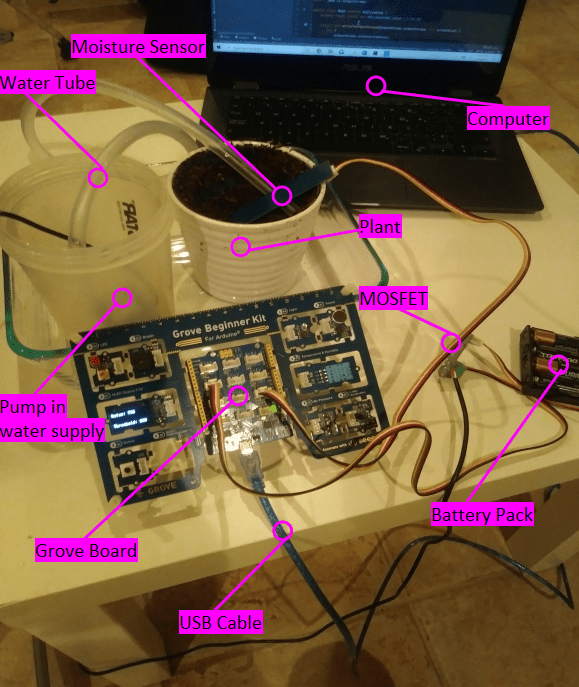
Annotated System
The same image of the plant watering system, with labels. This shows the all the different parts, like the moisture sensor, water pump, MOSFET (switch), battery pack, etc.
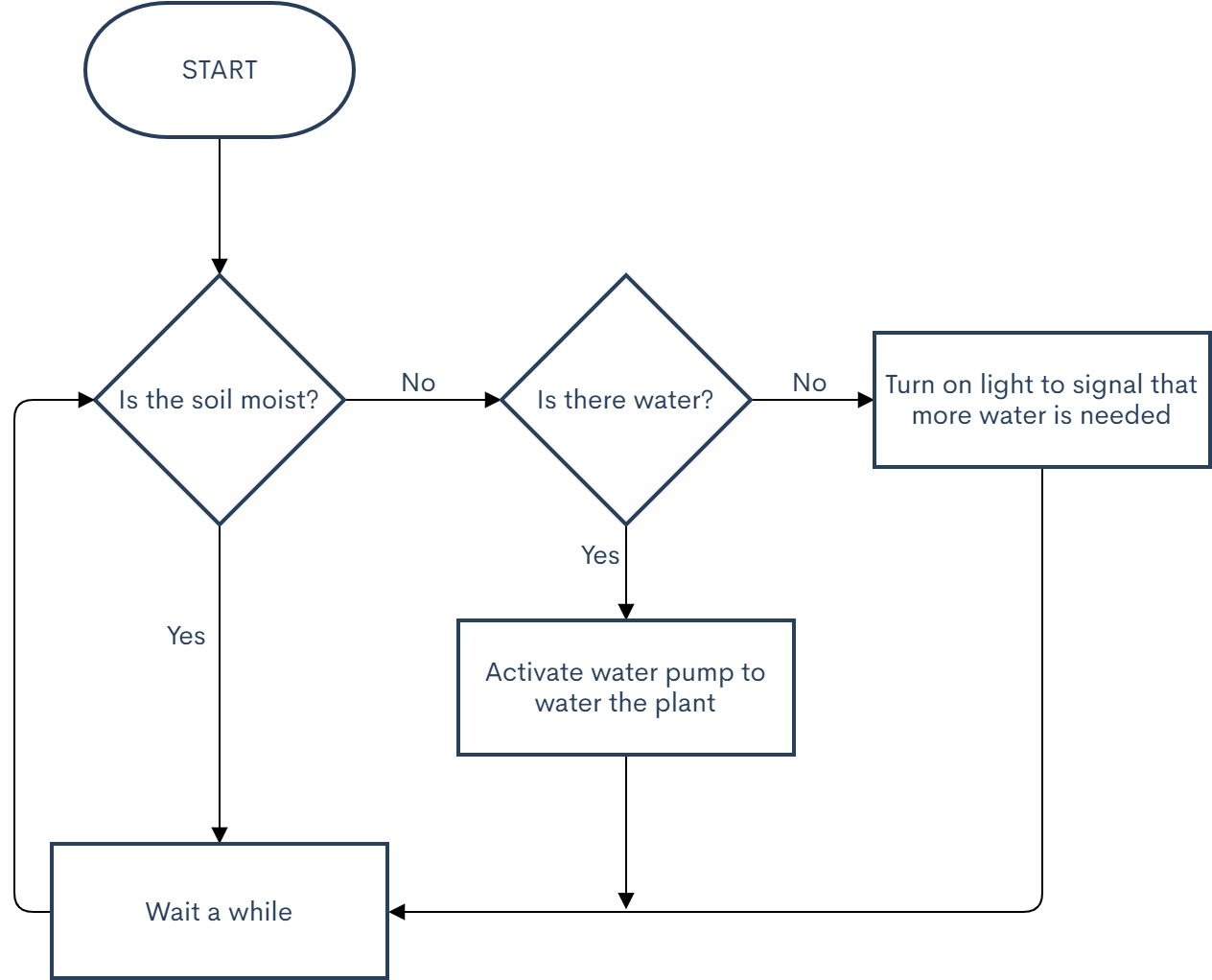
Flowchart of System
This is a flowchart describing a high-level overview of the flow of the the system. We check if the soil is moist, and if it is, we wait, then check again. Once the soil is dry, we check if there is water in the pump. If there is water, then activate the pump to water the plant. Otherwise, turn on the light to signal that more water is needed.
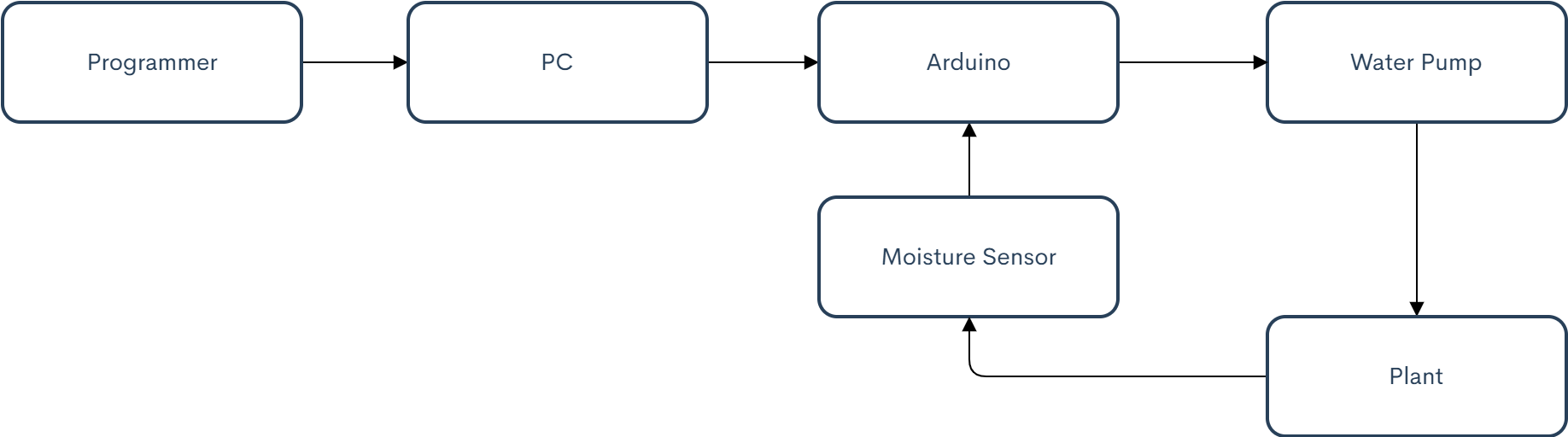
Components Illustration of System
This is a high-level diagram of the parts of the automated plant watering system. The programmer interacts with the PC, which sends the program to the Arduino. The Arduino interfaces with the plant through the moisture sensor (for collecting data), and the water pump (for watering the plant).
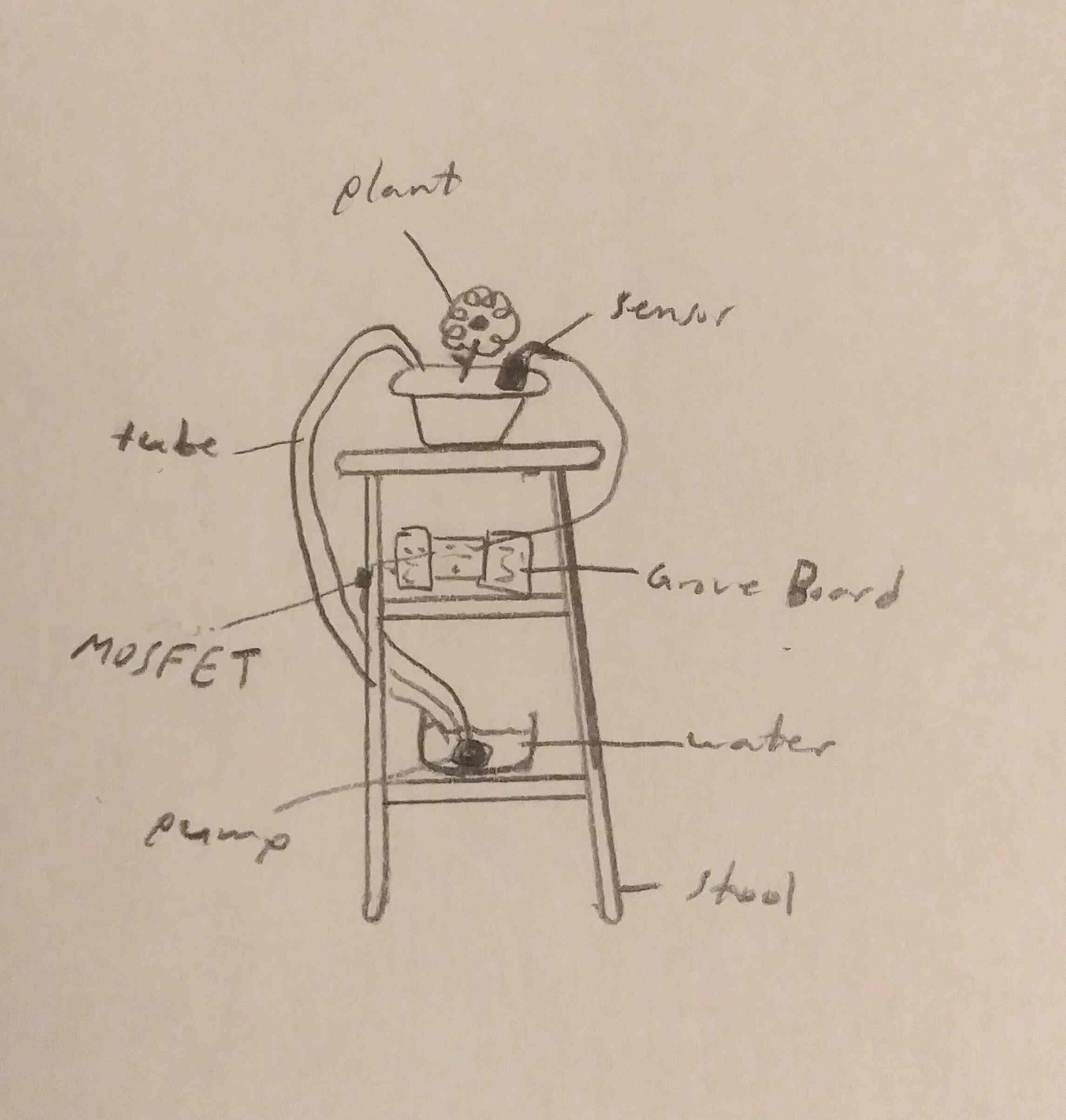
Drawing of the System
Before getting to work on the plant watering system, the project started with drawings and plans. This is a drawing of how the system would physically look, with the plant and the Arduino and all of its instruments.
Video Demonstration
How the Project Started
This project started as an assignment for a course at York University called Computational Thinking Through Mechatronics. Our final project in the course was to build a physical system that automates plant watering.
To do this, we used an Arduino-compatible board with a moisture sensor, a water pump, a MOSFET switch, and some other small components. We used C++ to program the board and we used MATLAB and Java to control the board from an external computer.
Essentially, the moisture sensor detects when the soil is dry, and the pump is used to water the plant when that occurs. This was controlled primarily through MATLAB and Java in an external computer, where we could also display data about soil measurements.
Extending the Project
After I finished the course, I realized that the external computer was not necessary for the basic soil monitoring and plant watering functionality. So, I decided to rewrite the C++ program on the board to handle this entirely, without any external computer running MATLAB or Java.
I also added functionality where information about the state of the soil is displayed on an OLED screen on the board. This acts as a substitute for the external computer's display of data.